The Integrated Rate Equation
The Integrated Rate Equation: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as First Order Reactions, Zero Order Reactions, Pseudo First Order Reactions, Time-Concentration Graph for Zero Order Reactions and, Time-Concentration Graphs for First Order Reactions
Important Questions on The Integrated Rate Equation
Half life for an order reaction involving reactant and
Give the value of .
Write the relation for half-life for a order reaction.
The half life for an order reaction involving reactant is given as:
Where, .
The half-life for an order reaction involving reactant is given as:
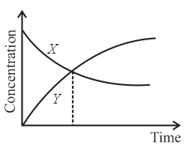
The accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species and for the elementary reaction as a function of time. The point of intersection of two curves represents:
The order of a reaction for which a linear line (with a negative slope) is obtained in a graph of vs is:
Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by titrating the liberated acetic acid against sodium hydroxide. The concentration of an ester at different temperatures is given below.
Show that it follows a pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains nearly constant during the course of the reaction. What is the value of in the equation ?
Show that the time required for completion of a first order reaction is three times the time required for completion.
The rate of the first order reaction products is , when reactant's concentration is . The rate constant for the reaction will be
The slope of the straight line obtained by plotting rate versus concentration of reactant for a first order reaction is.
The integrated rate equation for first order reaction products is given by
The unit of rate constant for first order reaction is
The rate of the reaction, products is when concentration of is Determine the rate constant if the reaction is
first order in .
The concentration of a reactant in a first order reaction products, varies with time as follows:
Show that the reaction is first order.
The rate constant of a certain first order reaction is . How many minutes does it take for the reactant concentration to drop to if the initial concentration of the reactant is ?
Describe the graphical representation of first order reaction.
What is zero order reaction? Write the differential rate law for the zero order reaction products. Derive its integrated rate law. How is it represented graphically?
Define integrated rate law. Derive the expression for integrated rate law for first order reaction products.
What is pseudo-first order reaction? Give one example.
You are required to determine the order and the rate constant for the following reaction:
How would you determine the value of rate constant from the graph?
